Smooth Sailing Ahead: Expertise at Your Helm
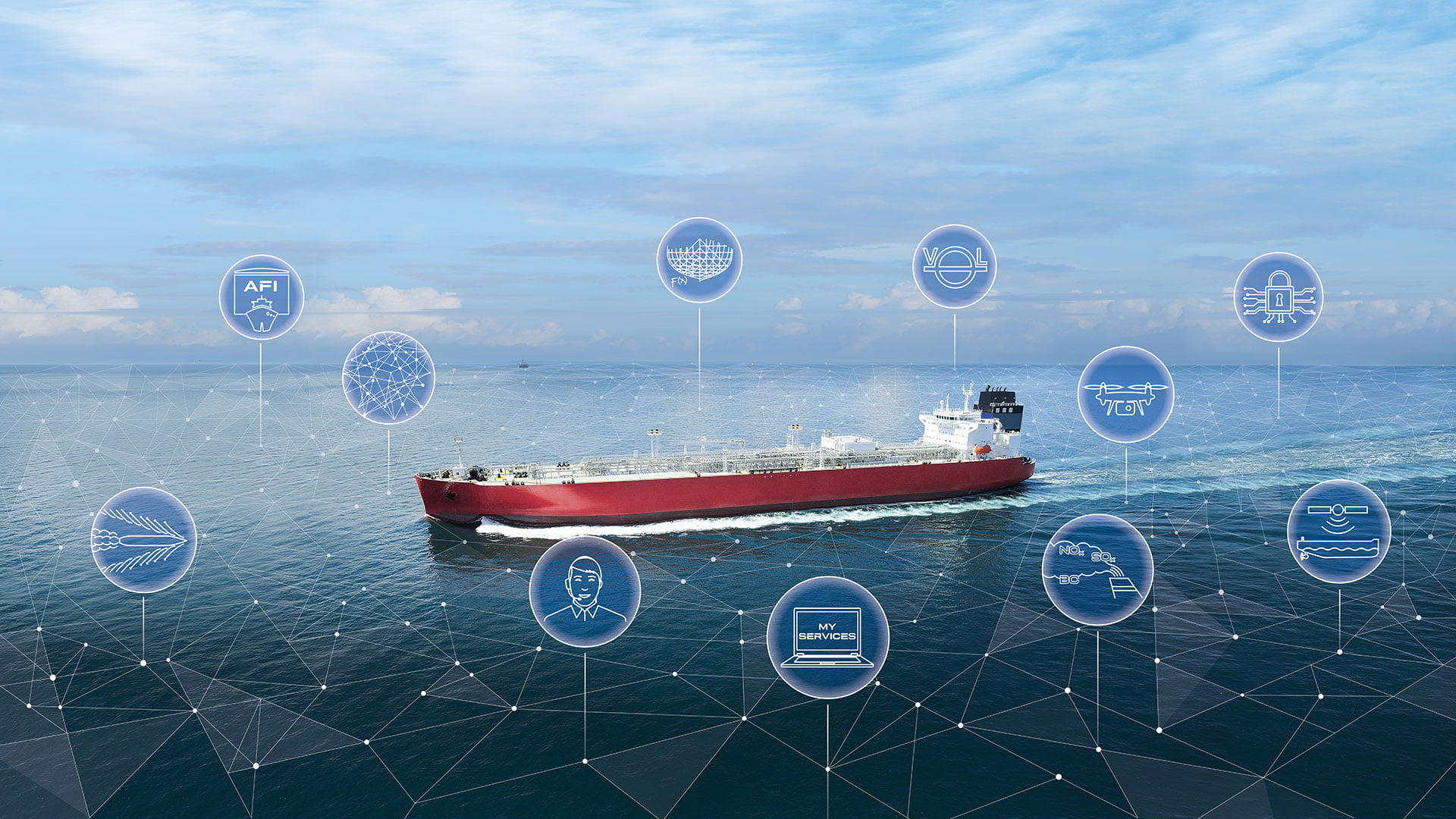
Digitalization and Automation
Assistance offered by AHA marine business
Sailing into the Future: Unlocking the Power of Marine Digitalization and Automation
Introduction:
Welcome to AHA Marine Business, where innovation meets excellence in the maritime industry. In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to explore the transformative potential of marine digitalization and automation, revolutionizing operations, enhancing efficiency, and charting a course towards a smarter, safer, and more sustainable maritime future.
1. The Promise of Marine Digitalization:
a. The Digital Revolution: The maritime industry is undergoing a digital revolution, driven by advances in technology, connectivity, and data analytics. From shipboard systems to shore-based operations, digitalization is transforming every aspect of the maritime value chain, unlocking new opportunities for efficiency, optimization, and innovation.
b. Key Drivers: Several key drivers are fueling the momentum towards marine digitalization, including increasing demand for efficiency and cost savings, regulatory requirements, safety and security concerns, and the need to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry landscape.
c. Benefits and Opportunities: Digitalization offers a myriad of benefits and opportunities for the maritime sector, including improved operational efficiency, enhanced safety and security, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced decision-making through real-time data analytics.
2. Understanding Marine Automation:
a. Evolution of Automation: Automation has been a key trend in the maritime industry for decades, with advancements in technology enabling greater levels of automation across various shipboard and shore-based operations. From engine automation to cargo handling systems, automation is revolutionizing how vessels are operated, managed, and maintained.
b. Types of Automation: Marine automation encompasses a wide range of systems and technologies, including autonomous vessels, remote monitoring and control systems, predictive maintenance solutions, and robotic automation for cargo handling and maintenance tasks.
c. Benefits and Challenges: While automation offers significant benefits in terms of efficiency, safety, and cost savings, it also presents challenges related to regulatory compliance, cybersecurity, workforce displacement, and the need for skilled personnel to operate and maintain automated systems.
3. The Role of Digitalization and Automation in Maritime Operations:
a. Navigation and Safety: Digitalization and automation are revolutionizing navigation and safety in the maritime sector, with technologies such as electronic charting systems, collision avoidance systems, and autonomous navigation systems improving situational awareness and reducing the risk of accidents and collisions.
b. Fleet Management: Digitalization and automation are transforming fleet management operations, enabling shipowners and operators to optimize vessel performance, monitor fuel consumption, track cargo shipments, and manage maintenance schedules more efficiently.
c. Cargo Handling and Logistics: Automation technologies such as robotic cranes, automated container terminals, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are revolutionizing cargo handling and logistics operations, reducing turnaround times, improving productivity, and enhancing supply chain efficiency.
d. Environmental Monitoring and Compliance: Digitalization and automation play a crucial role in environmental monitoring and compliance, with technologies such as emissions monitoring systems, ballast water management systems, and waste management systems enabling shipowners and operators to comply with environmental regulations and reduce their environmental footprint.
4. Implementing Digitalization and Automation Solutions:
a. Digitalization Strategy: Developing a digitalization strategy is essential for successfully implementing digitalization and automation solutions in the maritime sector. This strategy should align with business objectives, prioritize key initiatives, and consider factors such as technology readiness, regulatory requirements, and organizational capabilities.
b. Technology Selection: Selecting the right technology solutions is critical for achieving success in digitalization and automation initiatives. Shipowners and operators should evaluate available technologies based on factors such as functionality, reliability, scalability, and compatibility with existing systems.
c. Implementation Process: The implementation process for digitalization and automation solutions typically involves several stages, including planning, design, development, testing, deployment, and training. Effective project management, stakeholder engagement, and change management are essential for ensuring smooth implementation and adoption of new technologies.
d. Continuous Improvement: Digitalization and automation are ongoing processes that require continuous monitoring, evaluation, and optimization. Shipowners and operators should establish mechanisms for collecting and analyzing data, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing changes to optimize performance and achieve business objectives.
5. Case Studies:
a. Autonomous Shipping: A case study highlighting the successful implementation of autonomous shipping technology, resulting in improved efficiency, safety, and cost savings for a shipping company.
b. Remote Monitoring and Control: An example of a vessel equipped with remote monitoring and control systems, enabling shipowners to monitor vessel performance, diagnose issues, and make real-time adjustments from shore.
c. Predictive Maintenance: A case study showcasing a predictive maintenance solution that uses data analytics and machine learning algorithms to predict equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
6. Challenges and Considerations:
a. Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory compliance is a key consideration for digitalization and automation initiatives in the maritime sector, with regulations such as the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) guidelines for autonomous shipping and cybersecurity requirements for digital systems.
b. Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity is a growing concern in the maritime industry, with increased connectivity and reliance on digital systems making vessels vulnerable to cyber threats such as hacking, malware, and data breaches. Shipowners and operators must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect against cyber attacks and ensure the integrity and security of their digital systems.
c. Workforce Transition: The transition to digitalization and automation may require changes to the maritime workforce, including upskilling and reskilling of personnel to operate and maintain new technologies. Shipowners and operators must invest in training and development programs to ensure that their workforce is prepared for the digital future.
d. Ethical and Societal Implications: Digitalization and automation raise ethical and societal implications related to job displacement, privacy concerns, and the impact on local communities. Shipowners and operators must consider these implications and engage with stakeholders to address concerns and ensure that digitalization and automation initiatives benefit society as a whole.
7. Conclusion:
In conclusion, marine digitalization and automation hold immense promise for transforming the maritime industry, improving efficiency, enhancing safety, and reducing environmental impact. At AHA Marine Business, we are committed to leveraging the power of digitalization and automation to help our clients navigate the challenges and opportunities of the digital age, charting a course towards a smarter, safer, and more sustainable maritime future.